Understanding Hepatitis: Awareness, Prevention, and Treatment
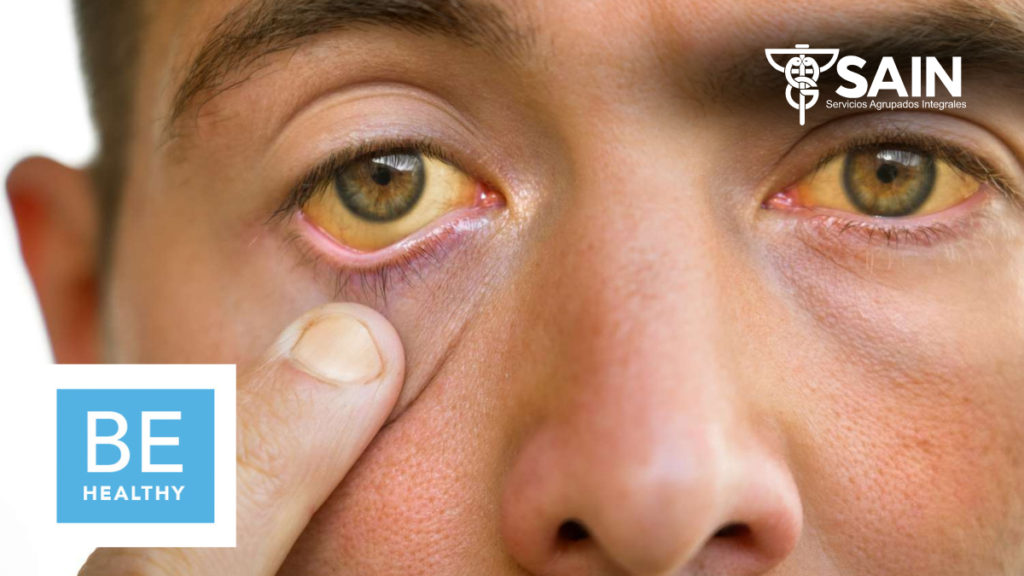
Hepatitis is a global health concern that affects millions of people each year. It is a term used to describe inflammation of the liver, which can be caused by a variety of factors, including viral infections, alcohol consumption, and certain medications. With the observance of World Hepatitis Day, it is important to increase awareness, promote prevention, and encourage early diagnosis and treatment. This blog will delve into the different types of hepatitis, their causes, symptoms, and ways to prevent and treat this condition.
Types of Hepatitis
There are five main types of viral hepatitis: A, B, C, D, and E. Each type is caused by a different virus and has distinct modes of transmission and outcomes.
- Hepatitis A (HAV):
– Transmission: Through consumption of contaminated food and water.
– Symptoms: Fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, and jaundice.
– Prevention: Vaccination, good hygiene practices, and safe food handling.
- Hepatitis B (HBV):
– Transmission: Through contact with infectious body fluids, such as blood, semen, and vaginal fluids.
– Symptoms: Acute symptoms are similar to HAV, but chronic HBV can lead to liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
– Prevention: Vaccination, safe sex practices, and avoiding sharing needles.
- Hepatitis C (HCV):
– Transmission: Primarily through blood-to-blood contact.
– Symptoms: Often asymptomatic in early stages but can lead to chronic liver disease.
– Prevention: There is no vaccine, so prevention focuses on safe injection practices and blood screening.
- Hepatitis D (HDV):
– Transmission: Requires HBV for replication; transmitted through contact with infectious body fluids.
– Symptoms: Similar to HBV but more severe.
– Prevention: HBV vaccination protects against HDV.
- Hepatitis E (HEV):
– Transmission: Through consumption of contaminated water.
– Symptoms: Similar to HAV, but can be more severe in pregnant women.
– Prevention: Good sanitation practices and safe drinking water.
Symptoms of Hepatitis
Hepatitis symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
– Fatigue
– Nausea and vomiting
– Abdominal pain
– Loss of appetite
– Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
– Dark urine
– Pale stool
– Joint pain
It is important to note that some people, especially those with chronic hepatitis B and C, may not exhibit symptoms until significant liver damage has occurred.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Treatment varies depending on the type of hepatitis:
– Hepatitis A and E: Often resolve on their own with supportive care, such as rest, hydration, and proper nutrition.
– Hepatitis B and D: Antiviral medications can help manage chronic infections and reduce liver damage.
– Hepatitis C: Advances in antiviral therapy have made it possible to cure most cases of HCV.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing hepatitis involves a combination of vaccination, safe practices, and public health measures:
– Vaccination: Effective vaccines are available for hepatitis A and B.
– Hygiene: Regular handwashing, safe food preparation, and clean drinking water can prevent HAV and HEV.
– Safe Practices: Using condoms, avoiding sharing needles, and ensuring safe blood transfusions can reduce the risk of HBV and HCV.
– Public Awareness: Education about transmission risks and prevention methods is crucial in combating the spread of hepatitis.
World Hepatitis Day serves as a reminder of the importance of awareness, prevention, and treatment of hepatitis. By understanding the different types of hepatitis, recognizing the symptoms, and adopting preventive measures, we can work towards a future free of this debilitating disease. Encourage your community to get vaccinated, practice safe hygiene, and seek medical advice if they suspect they have been exposed to hepatitis. Together, we can make a significant impact in the fight against hepatitis.
Contact us at +52 653 5367800 or email info@sainmedical.com
References:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.). Hepatitis. Retrieved from (https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/index.htm)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.). Hepatitis A. Retrieved from (https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hav/index.htm)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.). Hepatitis B. Retrieved from (https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hbv/index.htm)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.). Hepatitis C. Retrieved from (https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hcv/index.htm)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.). Hepatitis D. Retrieved from (https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hdv/index.htm)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.). Hepatitis E. Retrieved from (https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hev/index.htm)
- Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Hepatitis. Retrieved from (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hepatitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354289)
- American Liver Foundation. (n.d.). Diagnosis and Treatment of Hepatitis. Retrieved from (https://liverfoundation.org/for-patients/about-the-liver/diseases-of-the-liver/hepatitis/)
- World Health Organization. (n.d.). Hepatitis. Retrieved from (https://www.who.int/health-topics/hepatitis#tab=tab_1)





